Breast Cancer Prediction using Convolutional Neural Network for Beginners
Introduction:
It contains the following parts:
- Setup your environment
- Build your Breast Cancer classification model
- Model Validation
To run the program on your local computer, install the following required libraries, These libraries are
- python 3.8.0
- numpy
- pandas
- matplotlib
- scikit-learn
- tensorflow 2.0
- keras 2.3.0
Build your Breast Cancer classification model
Step 1: Understand the data
The first step of model prediction is to understand the data. It is more important to all machine learning and deep learning projects. You can find more information about the data, go to Breast Cancer Data.
Step 2: Import the Packages
Create a python file (for example model.py). After installed the required packages, import packages in your python file.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn import datasets, metrics
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from keras import Sequential
from keras.layers import Flatten, Dense, Dropout
from keras.layers import BatchNormalization
from keras.layers import Conv1D, MaxPool1D
Step 3: Import the dataNext, import the data using pandas
data = datasets.load_breast_cancer()
df = pd.DataFrame(data=data.data,
columns=data.feature_names)
X = df
y = data.target
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test =
train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2)print("Train_Data:")
print(X_train.shape)
print(y_train.shape)
print("\nTest_Data:")
print(X_test.shape)
print(y_test.shape)Out[]:
Train_Data:
(455, 30)
(455,)
Test_Data:
(114, 30)
(114,)
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_train = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = scaler.fit_transform(X_test)
Then, resize the data
X_train = X_train.reshape(455, 30, 1)
X_test = X_test.reshape(114, 30, 1)
We create model for breast cancer prediction model using convolutional neural network. It is type of deep learning networks. It is used for classification, segmentation and image processing problems. In this neural network, extract the features from input layer and perform mathematical convolutional operation.
epochs = 10
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv1D(32, 2,
activation='relu',
input_shape=(30,1)))
model.add(BatchNormalization())
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(Conv1D(64, 2, activation='relu'))
model.add(BatchNormalization())
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(64, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
- Sequential - appropriate for a plain stack of layers where each layer has exactly one input tensor and one output tensor.
- Conv1D - Convolutional one dimensional layer
- Batch Normalization - allows the network to do learning more independently. It is used to normalize the output of the previous layers.
- Flatten - matrix flatten to one dimensional array.
- Dense - fully connected neural network layer and it implement the operations.
- Activation - used through an activation layer, or through the activation argument supported by all forward layers.
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop',
loss='binary_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
history=model.fit(X_train,
y_train,
epochs = epochs,
validation_data = (X_test, y_test))
Out[]:
Train on 455 samples, validate on 114 samples
Epoch 1/10
455/455 [=========] - 8s 18ms/sample - loss: 0.2800 -
accuracy: 0.8835- val_loss: 0.4431- val_accuracy: 0.947
Epoch 2/10
455/455 [=========] - 1s 1ms/sample - loss: 0.1105 -
accuracy: 0.9582- val_loss: 0.3559 - val_accuracy: 0.929
Epoch 3/10
455/455 [=========] - 1s 1ms/sample - loss: 0.1102 -
accuracy: 0.9648- val_loss: 0.3136 - val_accuracy: 0.886
Epoch 4/10
455/455 [=========] - 1s 1ms/sample - loss: 0.1375 -
accuracy: 0.9604- val_loss: 0.3360 - val_accuracy: 0.842
Epoch 5/10
455/455 [=========] - 1s 1ms/sample - loss: 0.1137 -
accuracy: 0.9714- val_loss: 0.3202 - val_accuracy: 0.850
Epoch 6/10
455/455 [=========] - 1s 1ms/sample - loss: 0.0760 -
accuracy: 0.9802- val_loss: 0.3164 - val_accuracy: 0.842
Epoch 7/10
455/455 [=========] - 1s 1ms/sample - loss: 0.0655 -
accuracy: 0.9692- val_loss: 0.2960 - val_accuracy: 0.859
Epoch 8/10
455/455 [=========] - 1s 1ms/sample - loss: 0.0661 -
accuracy: 0.9758- val_loss: 0.3347 - val_accuracy: 0.850
Epoch 9/10
455/455 [=========] - 1s 1ms/sample - loss: 0.1068 -
accuracy: 0.9758- val_loss: 0.2602 - val_accuracy: 0.877
Epoch 10/10
455/455 [=========] - 1s 1ms/sample - loss: 0.0466 -
accuracy: 0.9846- val_loss: 0.2348 - val_accuracy: 0.903Model Validation
Finally, We created the model and then validate it.
test = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test, verbose=0)
print("Testing Accuracy: %.2f%%" % (test[1]*100))Out[]:
Testing Accuracy: 90.35%def plot_result(history, epoch):
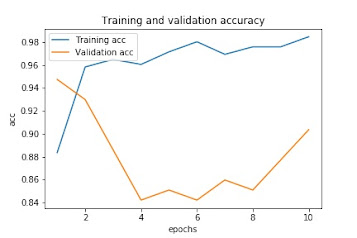
epoch_range = range(1, epoch+1)
plt.plot(epoch_range,
history.history['accuracy'],
label='Training acc')
plt.plot(epoch_range,
history.history['val_accuracy'],
label='Validation acc')
plt.title('Training and validation accuracy')
plt.xlabel('epochs')
plt.ylabel('acc')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
plt.plot(epoch_range,
history.history['loss'],
label='Training loss')
plt.plot(epoch_range,
history.history['val_loss'],
label='Validation loss')
plt.title('Training and validation loss')
plt.xlabel('epochs')
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()plot_result(history, epochs)Training and validation accuracy
Training and validation loss


No comments:
Post a Comment